Simply put, synethesia is a "neurological trait that combines two or more senses". Imagine being able to taste colour!
Let's watch this video that explains how it works:
Diagnosis
Although there is no officially established method of diagnosing synesthesia, some guidelines have been developed by Richard Cytowic, MD, a leading synesthesia researcher. Not everyone agrees on these standards, but they provide a starting point for diagnosis. According to Cytowic, synesthetic perceptions are: Involuntary: synesthetes do not actively think about their perceptions; they just happen.
Involuntary: synesthetes do not actively think about their perceptions; they just happen. Projected: rather than experiencing something in the "mind's eye," as might happen when you are asked to imagine a color, a synesthete often actually sees a color projected outside of the body.
Projected: rather than experiencing something in the "mind's eye," as might happen when you are asked to imagine a color, a synesthete often actually sees a color projected outside of the body. Durable and generic: the perception must be the same every time; for example, if you taste chocolate when you hear Beethoven's Violin Concerto, you must always taste chocolate when you hear it; also, the perception must be generic -- that is, you may see colors or lines or shapes in response to a certain smell, but you would not see something complex such as a room with people and furniture and pictures on the wall.
Durable and generic: the perception must be the same every time; for example, if you taste chocolate when you hear Beethoven's Violin Concerto, you must always taste chocolate when you hear it; also, the perception must be generic -- that is, you may see colors or lines or shapes in response to a certain smell, but you would not see something complex such as a room with people and furniture and pictures on the wall. Memorable: often, the secondary synesthetic perception is remembered better than the primary perception; for example, a synesthete who always associates the color purple with the name "Laura" will often remember that a woman's name is purple rather than actually remembering "Laura."
Memorable: often, the secondary synesthetic perception is remembered better than the primary perception; for example, a synesthete who always associates the color purple with the name "Laura" will often remember that a woman's name is purple rather than actually remembering "Laura." Emotional: the perceptions may cause emotional reactions such as pleasurable feelings.
Emotional: the perceptions may cause emotional reactions such as pleasurable feelings.Who has it?
Estimates for the number of people with synesthesia range from 1 in 200 to 1 in 100,000. There are probably many people who have the condition but do not realize what it is.
Synesthetes tend to be:
 Women: in the U.S., studies show that three times as many women as men have synesthesia; in the U.K., eight times as many women have been reported to have it. The reason for this difference is not known.
Women: in the U.S., studies show that three times as many women as men have synesthesia; in the U.K., eight times as many women have been reported to have it. The reason for this difference is not known. Left-handed: synesthetes are more likely to be left-handed than the general population.
Left-handed: synesthetes are more likely to be left-handed than the general population. Neurologically normal: synesthetes are of normal (or possibly above average) intelligence, and standard neurological exams are normal.
Neurologically normal: synesthetes are of normal (or possibly above average) intelligence, and standard neurological exams are normal. In the same family: synesthesia appears to be inherited in some fashion; it seems to be a dominant trait and it may be on the X-chromosome.
In the same family: synesthesia appears to be inherited in some fashion; it seems to be a dominant trait and it may be on the X-chromosome.Famous People
Some celebrated people who may have had synesthesia include:
 Vasily Kandinsky (painter, 1866-1944)
Vasily Kandinsky (painter, 1866-1944) Amy Beach (pianist and composer, 1867-1944)
Amy Beach (pianist and composer, 1867-1944) Olivier Messiaen (composer, 1908-1992)
Olivier Messiaen (composer, 1908-1992) Charles Baudelaire (poet, 1821-1867)
Charles Baudelaire (poet, 1821-1867) Franz Liszt (composer, 1811-1886)
Franz Liszt (composer, 1811-1886) Arthur Rimbaud (poet, 1854-1891)
Arthur Rimbaud (poet, 1854-1891) Richard Phillips Feynman (physicist, 1918-1988)
Richard Phillips Feynman (physicist, 1918-1988) Mary J. Blige (singer, songwriter, 1971-)
Mary J. Blige (singer, songwriter, 1971-)It is possible that some of these people merely expressed synesthetic ideas in their arts, although some of them undoubtedly did have synesthesia.
The Biological Basis of Synesthesia
Some scientists believe that synesthesia results from "crossed-wiring" in the brain. They hypothesize that in synesthetes, neurons and synapses that are "supposed" to be contained within one sensory system cross to another sensory system. It is unclear why this might happen but some researchers believe that these crossed connections are present in everyone at birth, and only later are the connections refined. In some studies, infants respond to sensory stimuli in a way that researchers think may involve synesthetic perceptions. It is hypothesized by these researchers that many children have crossed connections and later lose them. Adult synesthetes may have simply retained these crossed connections.
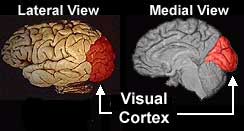
It is unclear which parts of the brain are involved in synesthesia. Richard Cytowic's research has led him to believe that the limbic system is primarily responsible for synesthetic experiences. The limbic systemincludes several brain structures primarily responsible for regulating our emotional responses. Other research, however, has shown significant activity in the cerebral cortex during synesthetic experiences. In fact, studies have shown a particularly interesting effect in the cortex: colored-hearing synesthetes have been shown to display activity in several areas of the visual cortex when they hear certain words. In particular, areas of the visual cortex associated with processing color are activated when the synesthetes hear words. Non-synesthetes do not show activity in these areas, even when asked to imagine colors or to associate certain colors with certain words.
A student directed me to the following article that is worth a read!
http://www.dazeddigital.com/artsandculture/article/28353/1/the-artist-who-battled-for-his-whole-life-hearing-colours
A student directed me to the following article that is worth a read!
http://www.dazeddigital.com/artsandculture/article/28353/1/the-artist-who-battled-for-his-whole-life-hearing-colours
Source: https://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/syne.html
No comments:
Post a Comment